Since the Financial crisis of 2008, central banks across the world have taken a more aggressive approach to doing their job. After combatting the economic turmoil in 2008 and 2020 with large-scale liquidity programs (otherwise known as quantitative easing), interest rate hikes have been the talk of the town lately.
Let’s walk through a situation many new traders find themselves in. Sudden, seemingly unexplainable market moves stopping out your trade, or worse. You struggle to find any explanation for the move until your friend points out the news of a new interest rate hike. The market reacted to the news, moving violently.
Many new traders get caught by surprise by such events. In this WOO article, we dive into the Federal Reserve, what they are and do, interest rate hikes, and how all of this affects the crypto markets.
What is the Federal Reserve (FED)?
The Federal Reserve (popularly referred to as Fed) is the Central Bank of the United States and is tasked with maintaining the US economy. To do this, the Fed strives to enable maximum employment, stable prices (stable, low inflation), and moderate interest rates in the US economy.
Essentially, it is the Fed’s job to make sure the economy of the United States can thrive. With stable prices, consumers can spend money without much worry, whereas maximum employment is the grease in the economic engine. By keeping interest rates moderate, borrowing is encouraged but does not get out of hand. Everything serves its purpose to maintain a balanced, and strong economy.
To maintain this balance, the Federal Reserve monitors the risk in the economy and keeps a close eye on prices and employment – to quickly react to any developments, using one of the several tools at their disposal.
What is Monetary Policy?
As we discussed, the Fed has several tools at its disposal, to steer the economy in the way they see fit. The way they use these tools is known as monetary policy – the rules set by the Federal Reserve (or another central bank!), aimed at controlling the supply of money, maximizing employment, ensuring stable prices and moderate interest rates.
Central Banks modify the monetary policy to combat inflation, and rising prices, encourage the creation of new jobs, or soften the effects of a recession. In other words, monetary policy is the toolbox central banks use to try to ensure a thriving economy.
In recent years, monetary policy tools like quantitative easing, open market operations, interest rate changes, and reserve requirements have been used a lot, but the Fed’s toolbox has more at its disposal.
What is an FOMC meeting?
FOMC meetings are where the Federal Reserve decides monetary policy. In their 8 meetings a year, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) discusses the economic situation and potential systemic risks and reviews whether the situation requires monetary policy alterations.
While the FOMC usually convenes 8 times a year, they may call for extra emergency meetings if pressing economic issues come up – such as the recent collapse of two major banks in the US: Silicon Valley Bank and the First Republic Bank.
The outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic lined up well with the usual schedule, where the committee acted swiftly and decisively without needing an emergency meeting. After the pandemic broke out, the FOMC kicked off the largest QE program in modern-day history – alleviating many of the short-term challenges.
After its initial success, the QE program had far-reaching consequences. Another challenge presented itself: skyrocketing inflation (peaking at 9.1% in June 2022), and the cost-of-living crisis many people are struggling with today. In recent months, battling those QE-induced challenges has been at the forefront of the FOMC Meeting agenda – and interest rate hikes are their primary tool of choice.
So, what are interest rate hikes?
Alright – lets dive into the main topic of today. The short answer is that interest rate hikes are when the central bank increases the current interest rate, but there is a little more to it.
The real answer to this question is that an interest rate hike is the term used to describe an increase in the federal funds rate – the interest rate at which commercial banks can lend money to one another, overnight. Contrary to most interest rates, the federal funds rate is set as a range, where banks can borrow or lend capital at rates between the upper and lower limit.
Since the Fed started combating inflation rates, 9 consecutive interest rates have taken place, pushing the upper limit of the federal funds rate from 0.25% to 5% in just over a year. The federal funds rate currently sits at 4.75% to 5.00%
What does a rate hike mean for the economy?
Interest rate hikes are designed to slow down the economy and curb inflation), by increasing the cost of capital. When the Fed hikes interest rates, it kicks off a chain reaction of cost increases. The rate hike itself makes borrowing more expensive for banks, who in turn raise the interest rates for their customers. Consequently, mortgages, commercial loans, and credit card debt charges skyrocket.
All in all, borrowing money becomes more expensive, and everyone will think twice before taking on additional debt. Essentially, interest rate hikes increase the cost of investing and spending – and therefore demand slows down.

As your economics professor has probably told you a million times, a decrease in demand makes the demand curve shift to the right – generally resulting in lower prices. In essence, an interest rate hike can be seen as an extinguisher to the inflation fire, it’s quite effective.
What does a rate hike mean for Crypto markets?
A rate hike does not just put the screws on inflation, though – its impact extends throughout the economy, and even financial markets. Over the past months, we’ve seen the stock market’s sensitivity to rate hike decisions, causing high volatility without failure. An interest rate cut generally pushes stock prices higher, as the cost of doing business goes down and publicly traded companies see their profitability increase as a result.
Conversely, interest rate hikes generally result in a downside, as the cost of business goes up and earnings take a haircut. This simple relationship between rate hikes and the stock market often spills over into crypto markets as well, as the two markets tend to correlate tightly around these events.
Nevertheless, the most noticeable effect of rate hikes lies in the volatility around the event – because of the psychological reaction to the news. The recent rate hike decision (on March 22) is a perfect example of this – where the market anticipated a rate hike pause and was caught by surprise by the ninth consecutive rate hike, resulting in close to 8% of downside after the news hit.
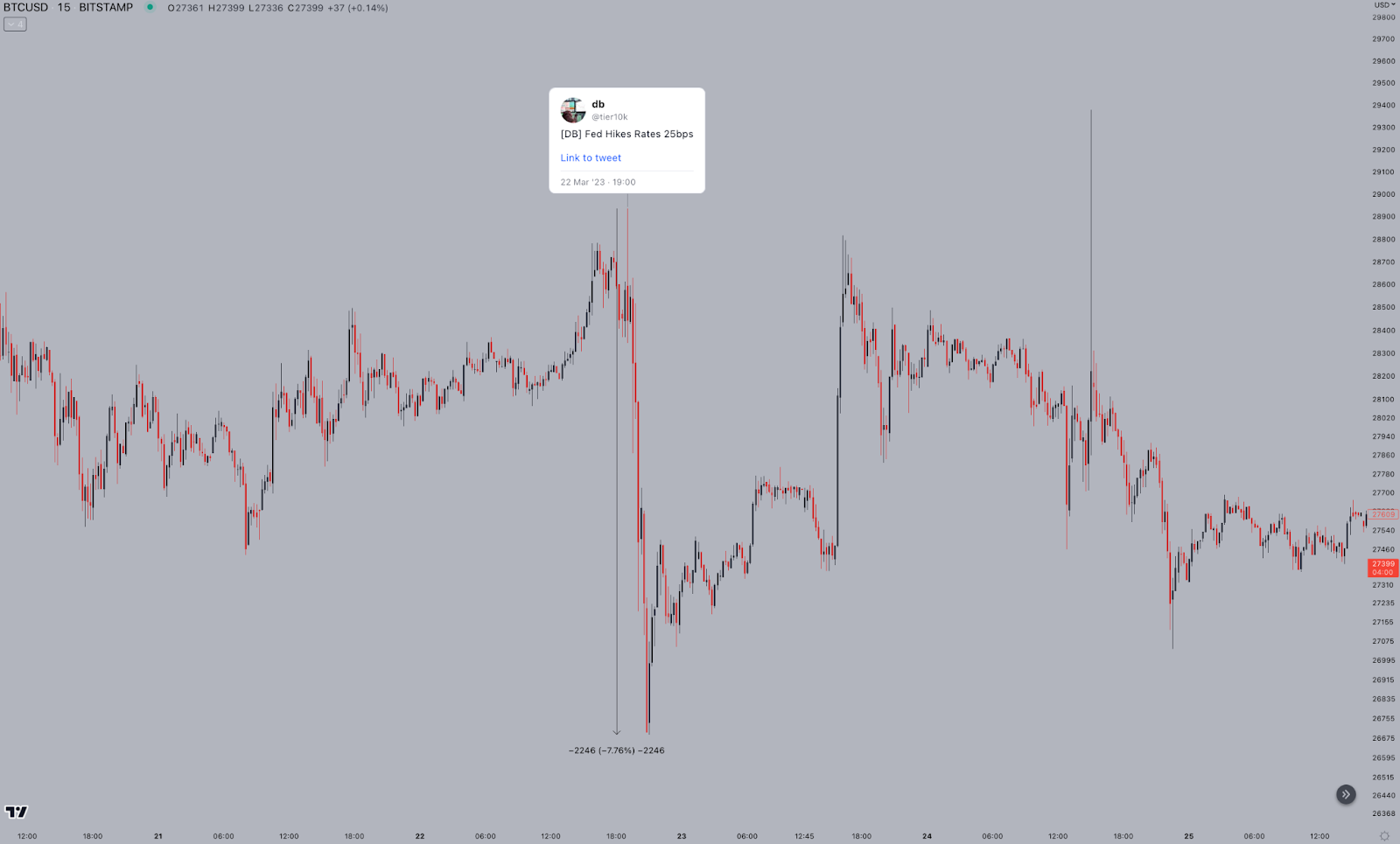
The psychological effect of rate hikes goes further than just short-term expectations, though. At the start of the current rate hike cycle, the market sold off heavily – as the Fed signalled a series of further rate hikes would follow. Essentially, the market started pricing in those further rate hikes as well. Now that we have seen nine consecutive rate hikes already, the odds of more rate hikes have decreased and markets are starting to get cautiously optimistic again. While the federal funds rate announcements still cause significant volatility, the market these days typically returns to the prices it traded at before the announcement.
Because of these psychological effects, it is likely that a rate hike pause or even a rate cut would cause much more volatility, than yet another rate hike. After all, it would be a strong change of tone, rather than a continuation of the current policy – and therefore a surprise. The market generally does not like surprises.
We recommend reading our article on the efficient market hypothesis, as it is closely related to this topic.
Conclusion
All in all, the Federal Reserve and FOMC hold a strong influence on both the stock and crypto markets. Predicting their decisions is nearly impossible, which is why trading these events is generally an unwise decision. However, it is recommended to study these economic driving forces, as they help you understand why markets move the way they do.
Writer’s Disclaimer: This article is based on my limited knowledge and experience. It has been written for educational purposes. It should not be construed as advice in any shape or form. Please do your own research.
Editor's note: CryptoJelleNL provides insights into the cryptocurrency industry. He has been actively participating in financial markets for over 5 years, primarily focusing on long-term investments in both the stock market and crypto. While he watches the returns of those investments roll in, he writes articles for multiple platforms. From now on, he will be contributing his insights for Alpha Circle as well.
Check out his twitter: twitter.com/cryptojellenl
—
The content above is neither a recommendation for investment and trading strategies nor does it constitute an investment offer, solicitation, or recommendation of any product or service. The content is for informational sharing purposes only. Anyone who makes or changes the investment decision based on the content shall undertake the result or loss by himself/herself.
The content of this document has been translated into different languages and shared throughout different platforms. In case of any discrepancy or inconsistency between different posts caused by mistranslations, the English version on our official website shall prevail.



